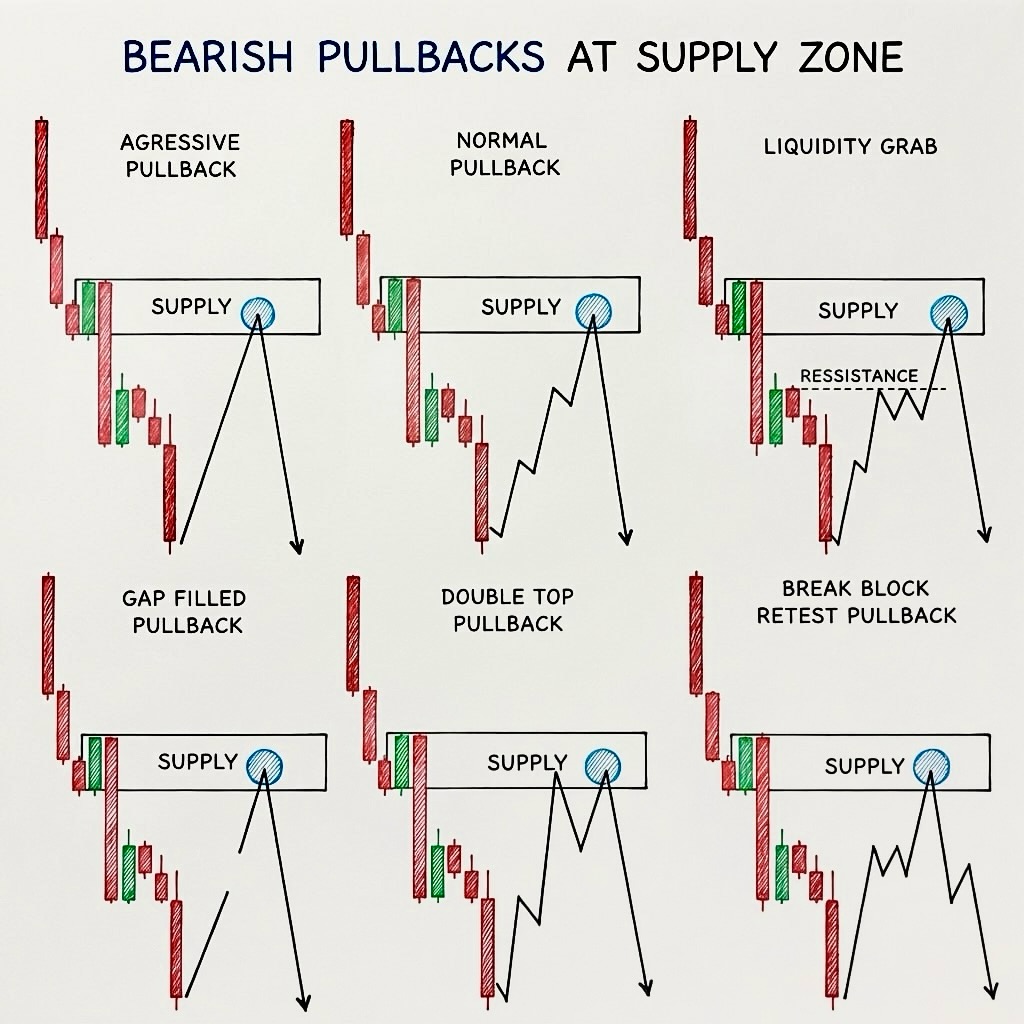
6 Bearish Pullbacks at Supply Zone – Beginner Breakdown
All six setups share the same idea: price drops from a supply zone (where sellers are strong), then pulls back up to retest that zone before continuing down. The difference is how the pullback looks.
1. Aggressive Pullback
Price barely pulls back — it touches the supply zone and immediately drops hard . Sellers are so dominant they don't even let buyers push price deep into the zone. Fast, sharp rejection. If you hesitate, you miss it.
2. Normal Pullback
Price gradually climbs back into the supply zone, spends a little time there with a few candles, then rolls over and drops. This is the "textbook" version — a clean, measured return to supply followed by a controlled reversal. Easiest to spot and trade.
3. Liquidity Grab
Price pulls back into supply and spikes slightly above it , sweeping past a resistance level. This fake breakout traps buyers who think price is breaking out. Once their stop-losses are collected, price reverses sharply downward. The spike above is the trap.
4. Gap Filled Pullback
Price dropped hard leaving a gap (Fair Value Gap/imbalance). The pullback comes back up specifically to fill that gap at the supply zone. Once the imbalance is filled, sellers step back in and price continues down.
5. Double Top Pullback
Price pulls back to supply twice , forming two roughly equal highs (a "double top" or "M" shape). The second rejection confirms sellers are defending the zone. The second failure to break through is your sell signal.
6. Breaker Block Retest Pullback
Price pulls back to a supply zone that also aligns with a breaker block — a previously broken support level that has now flipped into resistance. This confluence (supply + broken structure retest) makes it an especially high-probability short entry.
Key takeaway for beginners: The supply zone is the same in all six — what changes is the character of the pullback. Learning to recognize each type helps you stop hesitating and take the trade with confidence, because you'll know which flavor of pullback you're looking at in real time.