Flash Crash
Hello, this is Capital Cat!
Today, I will talk about the flash crash that occurred on January 3, 2019. This event is a classic example of a rapid market move in a short period, and it shocked many investors. Below is an easy-to-understand explanation.
Overview of the 2019 Flash Crash
- Date and time:January 3, 2019, early in the morning Japan time (around 5:00 AM)
- Currency pairs affected:
- USD/JPY(Dollar/Yen): fell rapidly from the 108 yen range to the 104 yen range
- AUD/JPY(Australian dollar/Yen): fell rapidly from the 80 yen range to the 72 yen range
- TRY/JPY(Turkish Lira/Yen): crashed from the 20 yen range to the 15 yen range
- Time:Dropped sharply within minutes and then quickly rebounded
Causes of the Flash Crash
- Liquidity decline:
- During year-end and New Year holidays, many market participants were on vacation, and especially in the early morning Japan time, it was a “thinly traded” period.
- Trading volume was lower than usual, making the market more susceptible to moves caused by a few large orders.
- Impact of algorithmic trading:
- Some algorithmic trading systems detected price movements and automatically triggered sell orders.
- These sell orders cascaded and accelerated the fall.
- Apple's downward revision of earnings outlook:
- Right before the flash crash, news that Apple had downwardly revised its earnings outlook shock the market.
- Global risk-off sentiment intensified, leading to selling in risk currencies like AUD and TRY.
- Chain reaction of stop losses:
- Investors’ stop-loss orders were triggered one after another, creating additional selling pressure.
Impact on the Market
- Damage to individual traders:
- The rapid fluctuation in a short time forced many traders to take losses due to margin calls.
- Large losses occurred particularly for investors using high leverage.
- Response of FX brokers:
- Many brokers widened spreads abnormally, and some orders did not get filled.
- Spread of risk aversion:
- The impact spread to stock and bond markets, and there was a temporary shift of funds from risk assets to safe havens.
Lesson: Preparing for Flash Crashes
Flash crashes occur suddenly, making them hard to predict, but you can mitigate risk with a few measures.
1. Avoid illiquid times
- It is prudent to refrain from trading or reduce positions during low-liquidity periods such as year-end holidays or early morning Japan time.
2. Set appropriate stop losses
- Set stop-loss orders to prevent unexpected losses. However, during low-liquidity periods, stop orders may be filled at unexpected prices, so consider setting them more wide-ranging.
3. Use modest leverage
- High leverage can lead to large losses from small price moves, so trade within a risk-controlled range.
4. Monitor information continuously
- When there are market news or important economic announcements, trade cautiously.
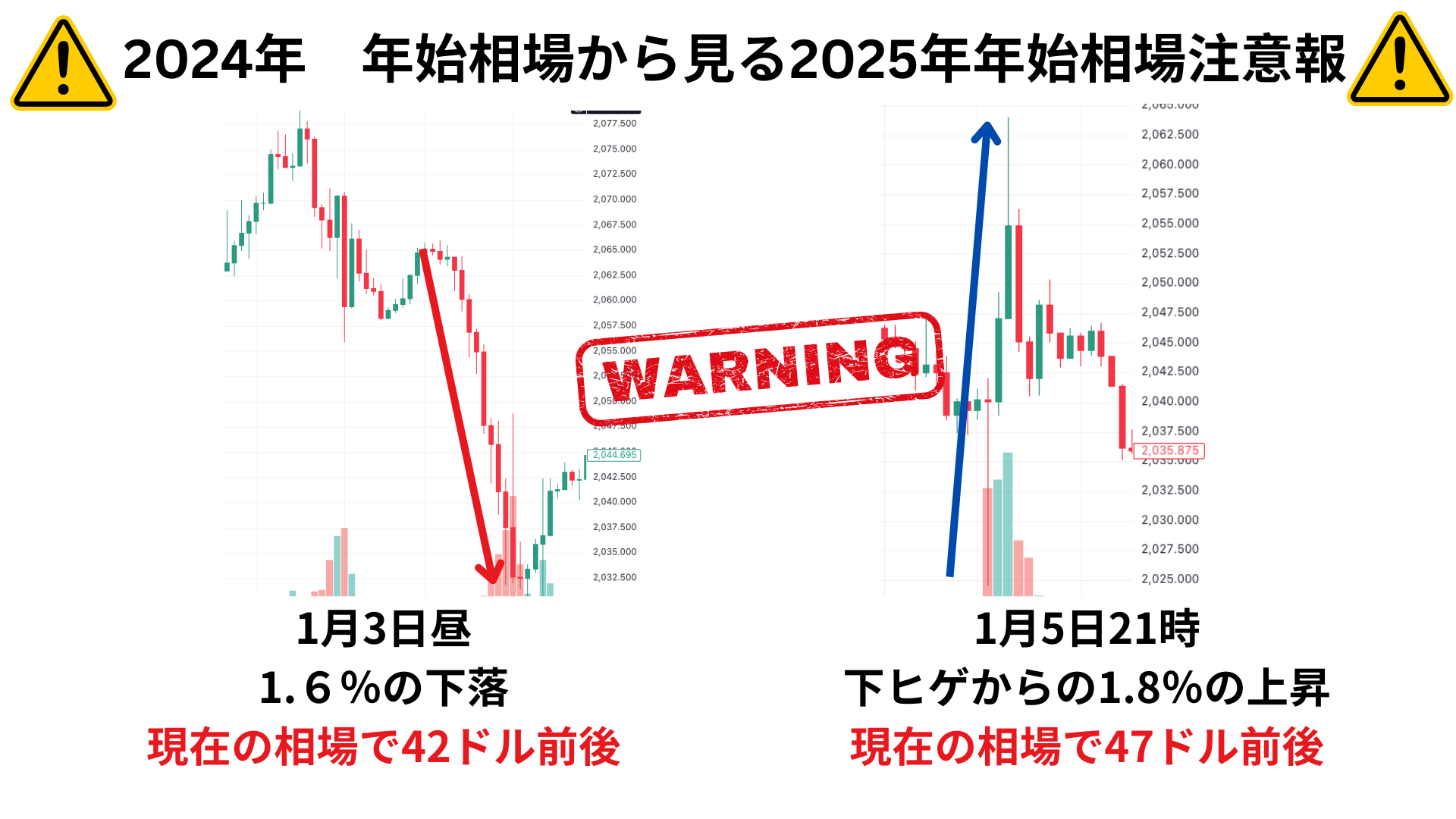
What will the gold market look like at the start of 2025?
The 2019 flash crash was largely influenced by liquidity thinning and cascading algorithmic trading. To avoid being caught in such sudden moves,thorough risk management and understanding the market characteristicsare important.
As an investor, calmly assess the situation and stay prepared to protect your assets! If you have any questions, feel free to ask anytime!
× ![]()