[Japanese translation] Yap Island Stone Money: Tracing Human History through Financial Technology and Blockchain

“Even if we throw it into the sea, our distributed ledger is in our heads, so it's OK; the value remains the same.”
What money that humans use has in common is “the fact that it itself has no intrinsic value.” Stones and banknotes basically have no value in themselves. They become vehicles of value becausewe choose to believe that, and that’s it. It’s very simple and nice, isn’t it (lol).
The latter part of the article describes the giant stone currency “ Rai stones” used on Yap Island in Micronesia, and I found it very interesting, as if I’d seen the roots of blockchain.
Since I’ve translated it, let’s read a little.
Tracing Human History through Financial Technology and Blockchain
The emergence of digital currencies does not merely evolve the concept of money. Italters the way we assess things, and thereby changes our behavioras well.If you want to know what is happening in the binary world behind cryptocurrencies, and how it will affect our future, you must start with historical studies.
Our world has entered an era of dramatic changes in the financial sector. Such changes are both progressive and revolutionary. We are building increasingly computer-supported commercial systems and continuously creating capabilities that can spark transformation. Our financial psychology must almost certainly evolve in line with such transactional system changes.
Smart environments in real life, virtual reality, quantum computers (including faster-than-light communication), artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and global distributed computers. All of the technologies being developed today hold the potential to bring about transformation.
If, in the relatively near future, we begin to use these technologies in combination, they will undoubtedly create complex effects across the world. Because the pace of technological development continues to accelerate rapidly, our understanding of history will be crucial for ensuring safety when implementing future technologies.
Blockchain is one of these revolutionary technologies and has become famous for the foundational functions of cryptocurrencies. Because blockchain stores and transmits data in a fair and neutral way, it is called a “trust machine.” With blockchain, the very nature of long-standing reliability has been questioned, and discussions about how peopleshould trust technologyhave become lively again.
Trust in computer infrastructure, information sources, and intermediaries suddenly became important. But building trust is more complicated than building protocols or systems. If people are unaware of their own importance or cannot trust their own autonomy, they will not recognize the benefits of blockchain.
There are many cases where technical safety measures and a lack of knowledge or expertise prevent adoption.The problem is how to secure sufficient trust from users over the long term and buy time for the technology to diffuse to a large number of people. More than mere invention or innovation, it is essential that the technology gradually permeates our civilization, building the groundwork needed for broad adoption.
Blockchain technology is entering our lives. It has certain features that can benefit a modern global society, but truly achieving widespread adoption may require leveraging it as the backbone of cryptocurrency systems.
Currently, cryptocurrencies sit on the periphery of our modern financial system, yet many countries and companies of various sizes are beginning to show interest in them. In fact, as the broad development of blockchain technology makes clear, its technical reliability is increasingly proving its value. Many people see this as the beginning of explosive adoption of technology, starting in the financial sector and reaching a peak in the coming years at a technological singularity.
If the financial sector is the foundation for the usefulness of blockchain, then blockchain must continually demonstrate its usefulness to move into other industries. So far, blockchain has prevailed in such efforts. To understand why, we must correctly grasp how blockchain is a natural consequence of human economic technology and a logical outcome of its development.
Humanity’s Financial Technology
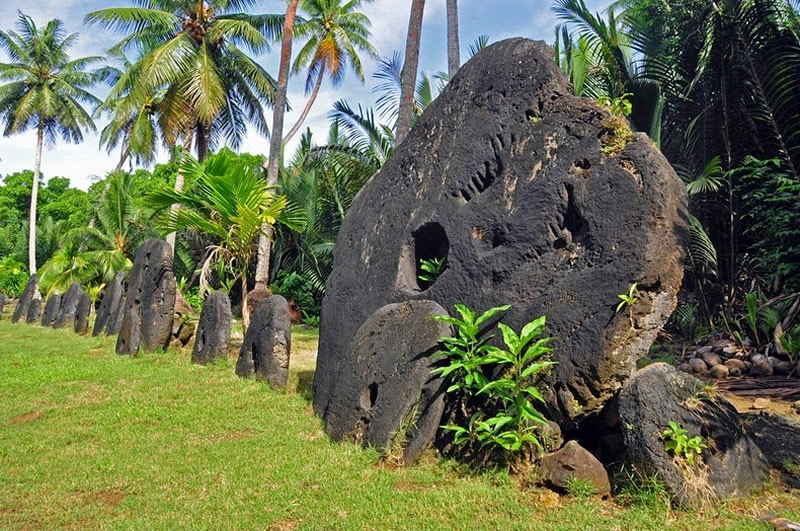 The history of money goes back to ancient times, but the most famous financial technology can be seen in the Micronesian culture of the 1900s. The inhabitants, known as Yapese, lived onYap Island in the Philippine Sea.
The history of money goes back to ancient times, but the most famous financial technology can be seen in the Micronesian culture of the 1900s. The inhabitants, known as Yapese, lived onYap Island in the Philippine Sea.Economists like Milton Friedman were intrigued and studied the monetary technology of Yap Island’s economy. This helps us understand theories about the true nature of money. Furthermorethe Yapese adopted forms of money that provide unique insights demonstrating that blockchain technology and even cryptocurrency are natural expressions of humanity’s financial technological evolution.
× ![]()