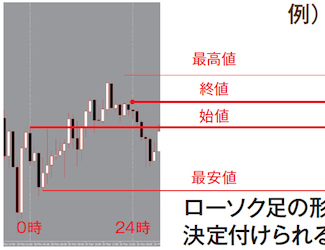
Financial literacy attained YEN Kura's Investment University (Academia) | Episode 9 [YEN Kura]
YEN Kura-san Profile
Enzō. Worked for over 20 years as a foreign exchange dealer at a US-based Citibank, the UK-based Standard Chartered Bank, and other foreign banks. Currently a top professional trader handling currency, Nikkei 225, Nikkei options, and individual stock trading. President and representative director of ADVANCE Co., Ltd., which primarily provides investment information. Deep expertise not only in major currencies such as the dollar and euro but also in dealing with emerging currencies, including Asian currencies. He also has strong ties with traders and fund executives overseas.
Newsletter:YENZOU Real Top Trading
Blog:YENZOU's FX Investment Techniques - Investing in the World with Dollars, Yen, Euro, Pound, and Australian Dollar
Twitter:https://twitter.com/YENZOU
*This article is a republication and editing of an article from FX Strategy.com October 2020 issue. Please note that the market information written in the body of the article may differ from current market conditions.
How Japan earns foreign currency
People of my generation learned in social studies class that “Japan is a trading nation, imports raw materials, manufactures products, exports them overseas, and earns foreign currency.” I think modern textbooks no longer describe it that way. Japan’s system of trade seems to have changed considerably from the past. So, how does Japan earn foreign currency from abroad? This month, let’s explore that area.
In macroeconomics dealing with international transactions, there is the concept of the balance of payments, which, like a company’s financial statements, totals the results of a country’s overseas transactions using double-entry bookkeeping. The international balance of payments statistics have been revised since January 2014 and consist of three components: current account, financial account, and capital transfers in the balance of payments.